NASA Earth observing system, under the name of EOS, is a coordinated network of satellites with a low slope intended for long-term, Global Terrestrial Observing, biosphere, atmosphere and oceans. EOS is a major component of the scientific department of NASA, It helps to better study the earth, thus providing valuable assistance to the world scientific community and the general public.
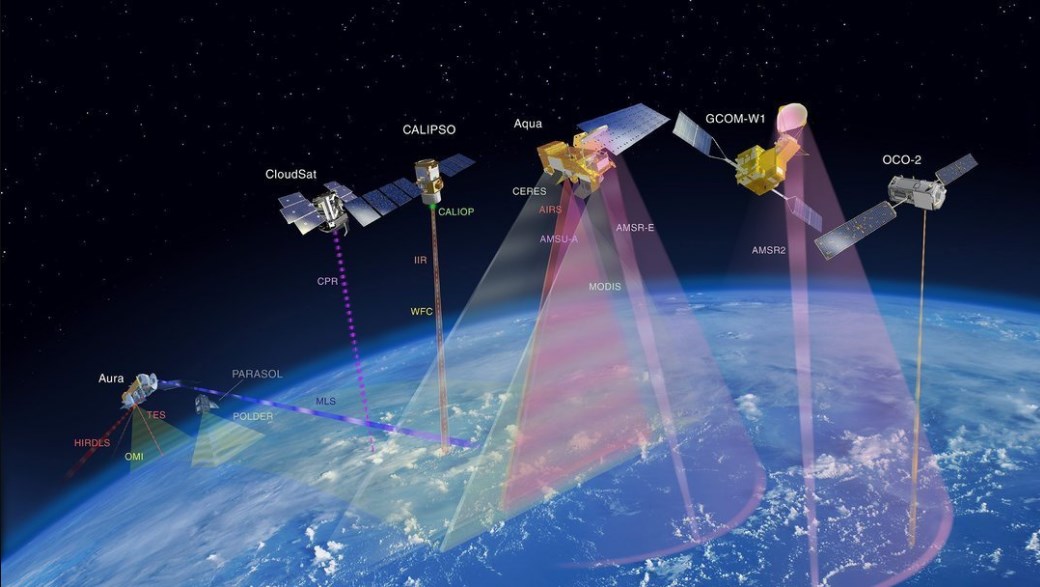
The purpose of surveillance systems for ground EOS
Хотя EOS (with English. translated as earth observation system) the start was given at the beginning of the 1980s, the actual results of the system began to give only in the early 1990s. Its main elements are the components of a network of satellites, they are intended for the monitoring and analysis of weather and climate events, as well as other research. Studies using EOS conducted to study:
- radiation;
- clouds;
- steam and precipitation;
- greenhouse gases;
- terrestrial hydrology and ecosystem processes;
- glaciers;
- ozone hole, stratosphere, and more.
EOS Platform

As a result, the development of earth observation system, компанией Макса Полякова была создана EOS Platform . It provides new opportunities for research:
- 3D modeling analyzed picture in real time;
- analysis of the image in real time;
- storage of large amounts of data;
- visualization and analysis.
Подробнее о возможностях EOS Platform можно узнать тут: http://gordonua.com/news/science/maks-polyakov-rasskazal-na-chto-sposobna-novaya-eos-platform-253072.html.
List of the mission and the date of the beginning

- Orbview-2 / SeaWiFS (частный сателлит с широким полем обзора ) – 1 August 1997 of the year;
- TRMM (Mission Tropical Rainfall measurement) – 27 November 1997 of the year;
- Landsat 7 – 15 April 1999 of the year;
- QuikSCAT (Quick Scatterometer) – 19 June 1999 of the year;
- Земля – 18 December 1999 of the year;
- ACRIMSat (мониторы Irdiance с активным кавитометрическим излучением ) – 20 December 1999 of the year;
- NMP/EO-1 (A new program of the Millennium / earth observation-1) – 21 November 2000 of the year;
- Jason 1 – 7 December 2001 of the year;
- METEOR 3M / Sage III – 10 December 2001 of the year;
- GRACE (gravity recovery and climate experiment in the field of) – 17 Martha 2002 of the year;
- Aqua – 4 May 2002 of the year;
- ADEOS II / Midori II (for the study of water satellite) – 12 December 2002 of the year – in October 2003 year destroyed by a solar storm;
- ICESat (satellite researched ice and clouds) – 12 January 2003;
- SORCE (Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment) – 25 January 2003;
- Аура – 15 July 2004 of the year;
- CloudSat – 28 April 2006 of the year;
- CALIPSO (Cloud satellite observations Pathfinder) – 28 April 2006 of the year;
- Hydros – scheduled for June 2006 of the year, but funding ran out in December 2005 of the year;
- OSTM (исследование поверхности океана Джейсон-2 ) – 20 June 2008 of the year;
- OCO (Orbiting Carbon Observatory) – 24 February 2009 of the year;
- Patron Saint Day – 4 Martha 2011 of the year, project failed;
- Водолей – 2010;
- АЭС «Суоми» (национальное полярно -орбитальное партнерство , anfangs NPOESS ). Подготовительный проект по экологической полярной орбитальной эксплуатационной экологической спутниковой системе – 28 September 2011 of the year;
- GPM (Global Precipitation Measurement) – 2013;
- LDCM (mission to ensure continuity of Landsat data) – 11 February 2013 of the year;
- NMP / EO-3 (новая программа тысячелетия / наблюдение Земли-3) – planned, now it is missing a start date.