Time, when the wheel alignment was limited only by adjusting the toe of the front wheels, gone forever. Along with vehicle improvements, eg, installation of multi-link independent suspension which improves handling and road holding, The way of calibrating the chassis has changed. Today it is no longer enough to make a toe-in, requires three-dimensional wheel geometry. Who cares?
Why you need to monitor your wheel alignment?
If you find, that the alignment in our car is incorrect, You should not hesitate to contact the appropriate service. It would be very dangerous to continue driving in this condition.. Faster tire wear is just a lower price, what you have to pay for ignoring symptoms, sent by the steering system.
Besides, you risk getting into a traffic accident, caused by a significant deterioration in the accuracy of the chassis. The car will be less stable in turns and will brake worse (smaller tire contact area with the road). The wear rate of elements will also increase significantly., responsible for the correct operation of the steering system (steering rods, tips, stabilizer links, steering gear). so, as we see, There is no point in postponing wheel alignment diagnostics..
In what cases is wheel alignment diagnosed??
What are the most common symptoms of geometry problems?
- The steering wheel is skewed - the car is driving straight, and the steering wheel is slightly or strongly turned to one side.
- While driving, the car pulls sideways.
- Vibration felt on the steering wheel.
- Noticeable differences between turning left and turning right.
- Worst car steering response.
Advantages of 3d wheel alignment
Unlike convergence, 3D geometry measurement allows you to visualize the position of the wheels in all planes in three dimensions. Thanks to the use of modern high-quality stands 3D CHAMBER TOE makes it possible to simultaneously measure the vertical and horizontal angle of the wheelbase, as well as track width.
Mechanic receives test results from 32 settings, which are compared with catalog values. If a lack of symmetry is detected, he is given precise instructions regarding, which plane should be corrected. Analysis is also carried out, pointing, why the results are not normative – perhaps, Damage has occurred and some element needs to be replaced. Typically, measurements using this technology are very fast., which also results in faster setup.
Regular inspection of the wheel geometry will significantly increase your safety and the service life of individual elements., which will eliminate the need for expensive repairs. It is recommended to carry out such inspection once a year as a preventative measure., which is not too burdensome, especially compared to the benefits.
How the 3D geometry of the chassis is checked?
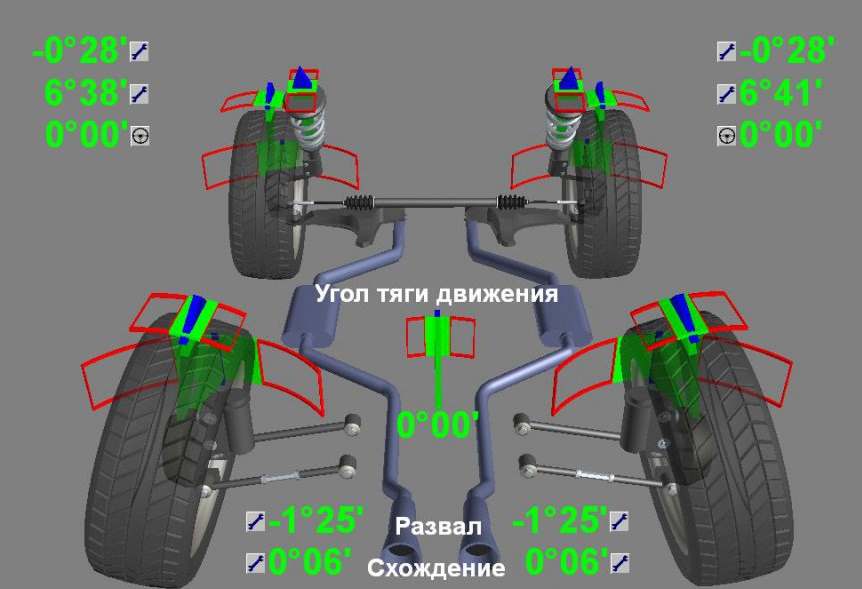
A mechanic installs measuring heads on a body in a plane, in which the axis of rotation of the wheel lies and which is perpendicular to the road surface. The plane rests on the side surface of the wheel well rim, as well as on the lower surface of the rim. Measuring heads are necessary for, so that the device measures the alignment of the car body in relation to the wheels or axle in the vertical and horizontal planes.
Popular instruments may have eight measuring heads, thanks to which they are able to measure values, characteristic of wheel geometry, which are usually not measured when setting toe. Based on the measurements taken, the device is able to determine the position of the body in horizontal and vertical planes, as well as in relation to the axle and wheels of the vehicle in an angular or linear meter.
Passive heads, mounted on wheels, and heads, fixed to the body on each wheel, controlled by cameras. After installing the heads, the system is calibrated for the given vehicle, to avoid mistakes. After correct calibration, a number of sub-procedures are used, thanks to which the system provides all feedback, eg:
- procedure for measuring the advance angles and inclination of the controlled axis;
- After measuring the alignment angles of the wheels and axles of the car, the program compares the values with the values, specified by the manufacturer, and defines, what values require adjustment. The program also offers a sequence of actions taking into account the technological sequence;
- procedure for toeing the front wheels without locking in a horizontal position. It's worth turning the steering wheel, and the device will measure the toe-in of the front wheels. The diagnostician then adjusts the left wheel, observing the position of the right wheel. Then adjust the right wheel, also watching the left wheel. After the wheels are aligned, the toe-in angles are measured again.;
- procedure for adjusting the camber and approach angles of the steered axle with the wheels removed. The head is attached to the wheel hub, and during adjustment the measurement takes place in real mode;
- procedure for adjusting the camber and advance angles of the steered axle using shims or eccentrics. The program selects the thickness of the washers or indicates the setting of the eccentrics;
- procedure for adjusting the camber angle of the rear axle and wheels using shimmers.
This is only a small part of it, what modern 3D WHEEL ALIGNMENT STANDS can do.












